
脑机接口(BCI)使用神经活动作为控制信号,实现与计算机的直接通信。这种神经信号通常是从各种研究透彻的脑电图(EEG)信号中挑选出来的。卷积神经网络(CNN)主要用来自动特征提取和分类,其在计算机视觉和语音识别领域中的使用已经很广泛。CNN已成功应用于基于EEG的BCI;但是,CNN主要应用于单个BCI范式,在其他范式中的使用比较少,论文作者提出是否可以设计一个CNN架构来准确分类来自不同BCI范式的EEG信号,同时尽可能地紧凑(定义为模型中的参数数量)。
该论文介绍了EEGNet,这是一种用于基于EEG的BCI的紧凑型卷积神经网络。论文介绍了使用深度和可分离卷积来构建特定于EEG的模型,该模型封装了脑机接口中常见的EEG特征提取概念。论文通过四种BCI范式(P300视觉诱发电位、错误相关负性反应(ERN)、运动相关皮层电位(MRCP)和感觉运动节律(SMR)),将EEGNet在主体内和跨主体分类方面与目前最先进的方法进行了比较。结果显示,在训练数据有限的情况下,EEGNet比参考算法具有更强的泛化能力和更高的性能。同时论文也证明了EEGNet可以有效地推广到ERP和基于振荡的BCI。
实验结果如下图,P300数据集的所有CNN模型之间的差异非常小,但是MRCP数据集却存在显著的差异,两个EEGNet模型的性能都优于所有其他模型。对于ERN数据集来说,两个EEGNet模型的性能都优于其他所有模型(p < 0.05)。
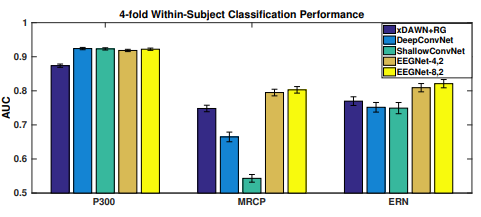
EEGNet网络原理
EEGNet网络结构图:
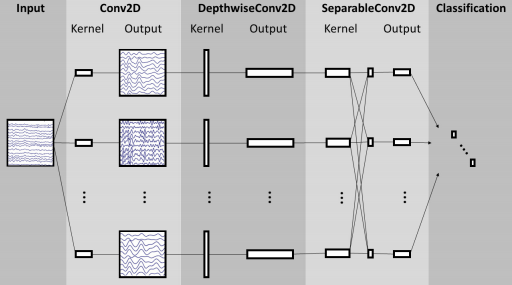
EEGNet原理架构如下:
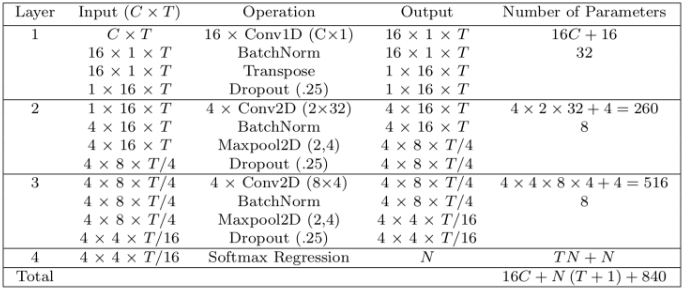
EEGNet网络实现
- import numpy as np
- from sklearn.metrics import roc_auc_score, precision_score, recall_score, accuracy_score
- import torch
- import torch.nn as nn
- import torch.optim as optim
- from torch.autograd import Variable
- import torch.nn.functional as F
- import torch.optim as optim
定义网络模型:
- class EEGNet(nn.Module):
- def __init__(self):
- super(EEGNet, self).__init__()
- self.T = 120
-
-
- # Layer 1
- self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(1, 16, (1, 64), padding = 0)
- self.batchnorm1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(16, False)
-
-
- # Layer 2
- self.padding1 = nn.ZeroPad2d((16, 17, 0, 1))
- self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(1, 4, (2, 32))
- self.batchnorm2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(4, False)
- self.pooling2 = nn.MaxPool2d(2, 4)
-
-
- # Layer 3
- self.padding2 = nn.ZeroPad2d((2, 1, 4, 3))
- self.conv3 = nn.Conv2d(4, 4, (8, 4))
- self.batchnorm3 = nn.BatchNorm2d(4, False)
- self.pooling3 = nn.MaxPool2d((2, 4))
-
-
- # 全连接层
- # 此维度将取决于数据中每个样本的时间戳数。
- # I have 120 timepoints.
- self.fc1 = nn.Linear(4*2*7, 1)
-
-
-
-
- def forward(self, x):
- # Layer 1
- x = F.elu(self.conv1(x))
- x = self.batchnorm1(x)
- x = F.dropout(x, 0.25)
- x = x.permute(0, 3, 1, 2)
-
-
- # Layer 2
- x = self.padding1(x)
- x = F.elu(self.conv2(x))
- x = self.batchnorm2(x)
- x = F.dropout(x, 0.25)
- x = self.pooling2(x)
-
-
- # Layer 3
- x = self.padding2(x)
- x = F.elu(self.conv3(x))
- x = self.batchnorm3(x)
- x = F.dropout(x, 0.25)
- x = self.pooling3(x)
-
-
- # 全连接层
- x = x.view(-1, 4*2*7)
- x = F.sigmoid(self.fc1(x))
- return x
定义评估指标:
acc:准确率
auc:AUC 即 ROC 曲线对应的面积
recall:召回率
precision:精确率
fmeasure:F值
- def evaluate(model, X, Y, params = ["acc"]):
- results = []
- batch_size = 100
-
-
- predicted = []
-
-
- for i in range(len(X)//batch_size):
- s = i*batch_size
- e = i*batch_size+batch_size
-
-
- inputs = Variable(torch.from_numpy(X[s:e]))
- pred = model(inputs)
-
-
- predicted.append(pred.data.cpu().numpy())
-
-
- inputs = Variable(torch.from_numpy(X))
- predicted = model(inputs)
- predicted = predicted.data.cpu().numpy()
- """
- 设置评估指标:
- acc:准确率
- auc:AUC 即 ROC 曲线对应的面积
- recall:召回率
- precision:精确率
- fmeasure:F值
- """
- for param in params:
- if param == 'acc':
- results.append(accuracy_score(Y, np.round(predicted)))
- if param == "auc":
- results.append(roc_auc_score(Y, predicted))
- if param == "recall":
- results.append(recall_score(Y, np.round(predicted)))
- if param == "precision":
- results.append(precision_score(Y, np.round(predicted)))
- if param == "fmeasure":
- precision = precision_score(Y, np.round(predicted))
- recall = recall_score(Y, np.round(predicted))
- results.append(2*precision*recall/ (precision+recall))
- return results
构建网络EEGNet,并设置二分类交叉熵和Adam优化器
- # 定义网络
- net = EEGNet()
- # 定义二分类交叉熵 (Binary Cross Entropy)
- criterion = nn.BCELoss()
- # 定义Adam优化器
- optimizer = optim.Adam(net.parameters())
创建数据集
- """
- 生成训练数据集,数据集有100个样本
- 训练数据X_train:为[0,1)之间的随机数;
- 标签数据y_train:为0或1
- """
- X_train = np.random.rand(100, 1, 120, 64).astype('float32')
- y_train = np.round(np.random.rand(100).astype('float32'))
- """
- 生成验证数据集,数据集有100个样本
- 验证数据X_val:为[0,1)之间的随机数;
- 标签数据y_val:为0或1
- """
- X_val = np.random.rand(100, 1, 120, 64).astype('float32')
- y_val = np.round(np.random.rand(100).astype('float32'))
- """
- 生成测试数据集,数据集有100个样本
- 测试数据X_test:为[0,1)之间的随机数;
- 标签数据y_test:为0或1
- """
- X_test = np.random.rand(100, 1, 120, 64).astype('float32')
- y_test = np.round(np.random.rand(100).astype('float32'))
训练并验证
- batch_size = 32
- # 训练 循环
- for epoch in range(10):
- print("\nEpoch ", epoch)
- running_loss = 0.0
- for i in range(len(X_train)//batch_size-1):
- s = i*batch_size
- e = i*batch_size+batch_size
-
-
- inputs = torch.from_numpy(X_train[s:e])
- labels = torch.FloatTensor(np.array([y_train[s:e]]).T*1.0)
-
-
- # wrap them in Variable
- inputs, labels = Variable(inputs), Variable(labels)
-
-
- # zero the parameter gradients
- optimizer.zero_grad()
-
-
- # forward + backward + optimize
- outputs = net(inputs)
- loss = criterion(outputs, labels)
- loss.backward()
-
-
- optimizer.step()
-
-
- running_loss += loss.item()
-
-
- # 验证
- params = ["acc", "auc", "fmeasure"]
- print(params)
- print("Training Loss ", running_loss)
- print("Train - ", evaluate(net, X_train, y_train, params))
- print("Validation - ", evaluate(net, X_val, y_val, params))
- print("Test - ", evaluate(net, X_test, y_test, params))
- Epoch 0
- ['acc', 'auc', 'fmeasure']
-
-
- Training Loss 1.6107637286186218
- Train - [0.52, 0.5280448717948718, 0.6470588235294118]
- Validation - [0.55, 0.450328407224959, 0.693877551020408]
- Test - [0.54, 0.578926282051282, 0.6617647058823529]
-
-
- Epoch 1
- ['acc', 'auc', 'fmeasure']
- Training Loss 1.5536684393882751
- Train - [0.45, 0.41145833333333337, 0.5454545454545454]
- Validation - [0.55, 0.4823481116584565, 0.6564885496183207]
- Test - [0.65, 0.6530448717948717, 0.7107438016528926]
-
-
- Epoch 2
- ['acc', 'auc', 'fmeasure']
- Training Loss 1.5197088718414307
- Train - [0.49, 0.5524839743589743, 0.5565217391304348]
- Validation - [0.53, 0.5870279146141215, 0.5436893203883495]
- Test - [0.57, 0.5428685897435898, 0.5567010309278351]
-
-
- Epoch 3
- ['acc', 'auc', 'fmeasure']
- Training Loss 1.4534167051315308
- Train - [0.53, 0.5228365384615385, 0.4597701149425287]
- Validation - [0.5, 0.48152709359605916, 0.46808510638297873]
- Test - [0.61, 0.6502403846153847, 0.5517241379310345]
-
-
- Epoch 4
- ['acc', 'auc', 'fmeasure']
- Training Loss 1.3821702003479004
- Train - [0.46, 0.4651442307692308, 0.3076923076923077]
- Validation - [0.47, 0.5977011494252874, 0.29333333333333333]
- Test - [0.52, 0.5268429487179488, 0.35135135135135137]
-
-
- Epoch 5
- ['acc', 'auc', 'fmeasure']
- Training Loss 1.440490186214447
- Train - [0.56, 0.516025641025641, 0.35294117647058826]
- Validation - [0.36, 0.3801313628899836, 0.2]
- Test - [0.53, 0.6113782051282052, 0.27692307692307694]
-
-
- Epoch 6
- ['acc', 'auc', 'fmeasure']
- Training Loss 1.4722238183021545
- Train - [0.47, 0.4194711538461539, 0.13114754098360656]
- Validation - [0.46, 0.5648604269293925, 0.2285714285714286]
- Test - [0.5, 0.5348557692307693, 0.10714285714285714]
-
-
- Epoch 7
- ['acc', 'auc', 'fmeasure']
- Training Loss 1.3460421562194824
- Train - [0.51, 0.44871794871794873, 0.1694915254237288]
-
原文:https://blog.csdn.net/zyb228107/article/details/121882410

