Dubbo Bean加载
我们使用dubbo都是和Spring进行结合使用,并且常用的方式就是通过在xml中配置dubbo来实现的,我们结合这种方式来看一下,spring是如何加载dubbo的bean的,下面我们来看一下一个最基本的dubbo的配置,结合配置来分析:以下示例来自于官方例子
<beans xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:dubbo="http://dubbo.apache.org/schema/dubbo"
xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://dubbo.apache.org/schema/dubbo http://dubbo.apache.org/schema/dubbo/dubbo.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<context:property-placeholder/>
<dubbo:application name="demo-provider"/>
<dubbo:registry address="zookeeper://${zookeeper.address:127.0.0.1}:2181"/>
<bean id="demoService" class="org.apache.dubbo.samples.serialization.impl.DemoServiceImpl"/>
<dubbo:service interface="org.apache.dubbo.samples.serialization.api.DemoService" ref="demoService"
serialization="java"/>
beans>
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
在配置文件中配置了注册中心
- 编写一个Java Bean;
- 编写XSD文件;
- 编写标签解析器,实现BeanDefinitionParser接口;
- 编写注册标签解析器的NamespaceHandlerSupport,继承NamespaceHandlerSupport,重写init方法,注册自定义的标签解析器;
- 编写spring.handlers和spring.schemas文件;
开发完自定义的标签后就可以在spring配置文件中使用了,通过dubbo的spring.handlers文件找到注册标签解析器的类com.alibaba.dubbo.config.spring.schema.DubboNamespaceHandler。通过下面代码可以看到,dubbo注册了10个自定义标签,除了annotation标签,其他的标签均使用DubboBeanDefinitionParser解析器进行解析,解析dubbo的spring自定义标签后就是在Spring容器启动过程中创建对象和属性赋值。
public class DubboNamespaceHandler extends NamespaceHandlerSupport {
static {
Version.checkDuplicate(DubboNamespaceHandler.class);
}
@Override
public void init() {
registerBeanDefinitionParser("application", new DubboBeanDefinitionParser(ApplicationConfig.class, true));
registerBeanDefinitionParser("module", new DubboBeanDefinitionParser(ModuleConfig.class, true));
registerBeanDefinitionParser("registry", new DubboBeanDefinitionParser(RegistryConfig.class, true));
registerBeanDefinitionParser("monitor", new DubboBeanDefinitionParser(MonitorConfig.class, true));
registerBeanDefinitionParser("provider", new DubboBeanDefinitionParser(ProviderConfig.class, true));
registerBeanDefinitionParser("consumer", new DubboBeanDefinitionParser(ConsumerConfig.class, true));
registerBeanDefinitionParser("protocol", new DubboBeanDefinitionParser(ProtocolConfig.class, true));
registerBeanDefinitionParser("service", new DubboBeanDefinitionParser(ServiceBean.class, true));
registerBeanDefinitionParser("reference", new DubboBeanDefinitionParser(ReferenceBean.class, false));
registerBeanDefinitionParser("annotation", new AnnotationBeanDefinitionParser());
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
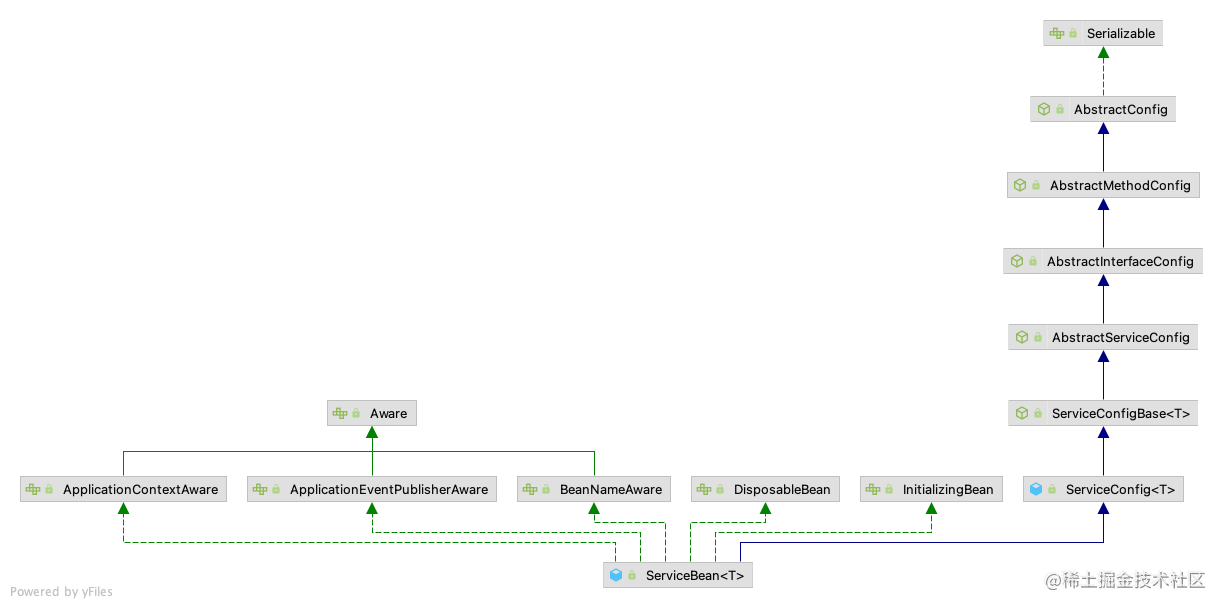
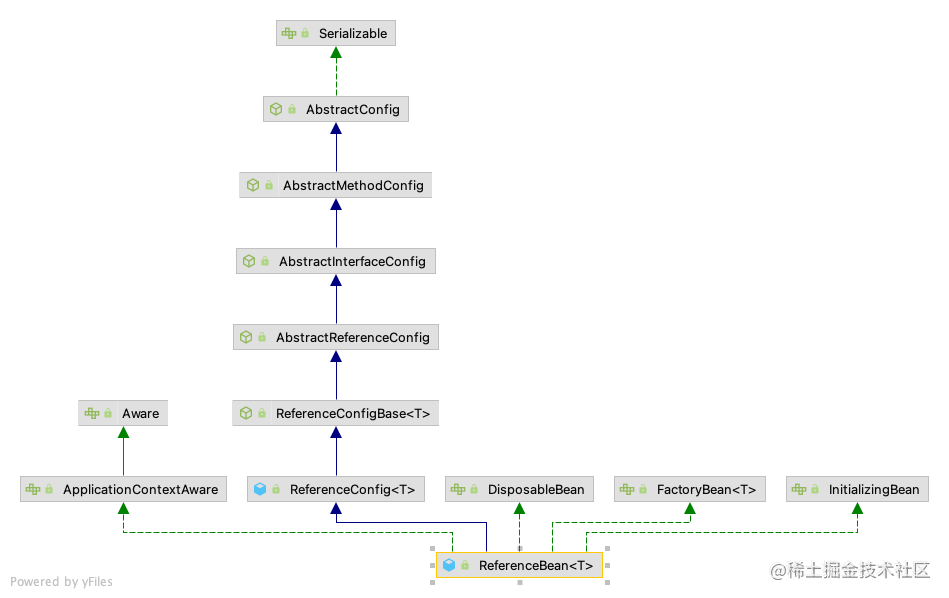
Dubbo生产者和消费者的核心类分别是ServiceBean和ReferenceBean,在spring解析
- ServiceBean
- ReferenceBean
Dubbo启动
在上面的dubbo的bean加载章节中我们知道dubbo通过Spring自定义标签在程序启动过程中实现了对bean的加载,接下来我们看一下Dubbo是如何启动的。
Dubbo客户端启动监听DubboBootstrapApplicationListener
上一章节说到了通过spring自定义标签已经创建了dubbo核心的bean,dubbo客户端启动的过程,dubbo用过实现了Spring的监听接口
ApplicationListener接口,监听Spring容器refresh刷新完成的事件。当Spring容器刷新完毕后Dubbo监听执行dubbo客户端启动,代码如下:
public class DubboBootstrapApplicationListener extends OneTimeExecutionApplicationContextEventListener
implements Ordered {
/**
* The bean name of {@link DubboBootstrapApplicationListener}
*
* @since 2.7.6
*/
public static final String BEAN_NAME = "dubboBootstrapApplicationListener";
private final DubboBootstrap dubboBootstrap;
public DubboBootstrapApplicationListener() {
// 获取DubboBootstrap对象,会通过SPI加载Environment,ConfigManager
this.dubboBootstrap = DubboBootstrap.getInstance();
}
@Override
public void onApplicationContextEvent(ApplicationContextEvent event) {
// 处理ContextRefreshedEvent时间,该事件是Spring容器刷新完毕时间
if (event instanceof ContextRefreshedEvent) {
onContextRefreshedEvent((ContextRefreshedEvent) event);
} else if (event instanceof ContextClosedEvent) {
// 处理ContextClosedEvent时间,spring上下文关闭事件
onContextClosedEvent((ContextClosedEvent) event);
}
}
// spring上下文刷新完毕事件
private void onContextRefreshedEvent(ContextRefreshedEvent event) {
dubboBootstrap.start();
}
// Spring上下文关闭事件
private void onContextClosedEvent(ContextClosedEvent event) {
dubboBootstrap.stop();
}
@Override
public int getOrder() {
return LOWEST_PRECEDENCE;
}
}
abstract class OneTimeExecutionApplicationContextEventListener implements ApplicationListener, ApplicationContextAware {
private ApplicationContext applicationContext;
public final void onApplicationEvent(ApplicationEvent event) {
if (isOriginalEventSource(event) && event instanceof ApplicationContextEvent) {
onApplicationContextEvent((ApplicationContextEvent) event);
}
}
/**
* The subclass overrides this method to handle {@link ApplicationContextEvent}
*
* @param event {@link ApplicationContextEvent}
*/
protected abstract void onApplicationContextEvent(ApplicationContextEvent event);
/**
* Is original {@link ApplicationContext} as the event source
*
* @param event {@link ApplicationEvent}
* @return
*/
private boolean isOriginalEventSource(ApplicationEvent event) {
return (applicationContext == null) // Current ApplicationListener is not a Spring Bean, just was added
// into Spring's ConfigurableApplicationContext
|| Objects.equals(applicationContext, event.getSource());
}
@Override
public final void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException {
this.applicationContext = applicationContext;
}
public ApplicationContext getApplicationContext() {
return applicationContext;
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
Spring容器刷新完毕发布事件代码如下:
/**
* Finish the refresh of this context, invoking the LifecycleProcessor's
* onRefresh() method and publishing the
* {@link org.springframework.context.event.ContextRefreshedEvent}.
*/
protected void finishRefresh() {
// Initialize lifecycle processor for this context.
initLifecycleProcessor();
// Propagate refresh to lifecycle processor first.
getLifecycleProcessor().onRefresh();
// Publish the final event.发布ContextRefreshedEvent事件
publishEvent(new ContextRefreshedEvent(this));
// Participate in LiveBeansView MBean, if active.
LiveBeansView.registerApplicationContext(this);
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
DubboBootstrap#start()dubbo启动
public DubboBootstrap start() {
// 是否启动过
if (started.compareAndSet(false, true)) {
ready.set(false);
// 初始化
initialize();
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info(NAME + " is starting...");
}
// 1. 发布dubbo服务
exportServices();
// Not only provider register,原数据发布一次
if (!isOnlyRegisterProvider() || hasExportedServices()) {
// 2. 发布元数据
exportMetadataService();
//3. Register the local ServiceInstance if required
registerServiceInstance();
}
referServices();
if (asyncExportingFutures.size() > 0) {
new Thread(() -> {
try {
this.awaitFinish();
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.warn(NAME + " exportAsync occurred an exception.");
}
ready.set(true);
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info(NAME + " is ready.");
}
}).start();
} else {
ready.set(true);
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info(NAME + " is ready.");
}
}
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info(NAME + " has started.");
}
}
return this;
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
总结
Dubbo + Spring的Bean加载流程通过自定义标签进行Bean的加载处理,Dubbo基于Spring自定义标签规范实现了标签解析器DubboBeanDefinitionParser和AnnotationBeanDefinitionParser,通过标签解析完成bean的创建,赋值,初始化等生命周期的处理,然后dubbo实现了Spring的监听器ApplicationListener,监听spring容器刷新完毕的事件,在spring容器刷新完毕后进行dubbo客户端的启动,来进行服务的注册,发布,订阅等。
